There is a significant movement to have iPhones manufactured in the United States. In theory, this could generate numerous jobs, […]
Category: Telecommunication
More Than 400,000 Wireless Phone Chargers Recalled Over Fire Hazard
Casely, a business located in Brooklyn, has received 51 notifications regarding lithium-ion batteries that are overheating, swelling, or catching fire, […]
If you’re planning to upgrade your electronics, you might want to buy them now – here’s why
On Wednesday, April 2, President Donald Trump declared that the United States would implement a new set of tariffs against […]
Want to extend your iPhone battery life? Stop making this common mistake
I have invested considerable time discussing that battery degradation is a natural occurrence, and increased usage leads to more wear […]
Are tariffs about to make your next iPhone way more expensive? It’s complicated
The recent trade tariffs imposed by the current US administration on “Liberation Day” against trade partners have raised concerns about […]
Apple is not the laggard in AI. AI is the laggard in AI
Apple has been facing considerable criticism in the tech and finance media due to its notably chaotic venture into artificial […]
Why get a smart watch?
They have become vital devices that assist in staying connected, monitoring your health, and streamlining your daily activities. Whether you’re […]
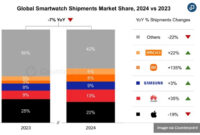
Global smartwatch sales fall for first time
Global sales of smartwatches have experienced a decline for the first time, new data reveals, largely driven by a significant […]
Red Hat talks 5G, 6G and the VMware effect
Rimma Iontel from Red Hat talks about how the company has ramped up investments in OpenShift Virtualization and what lies […]
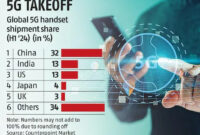
Asia drives budget 5G smartphone boom
There’s significant enthusiasm currently surrounding the latest premium smartphones from brands like Apple and Huawei, but what about the low-end […]
5G Devices Market Size & Share Analysis – Growth Trends & Forecasts (2025 – 2030)
The Global 5G Equipment Market is categorized by form factor (including Modules, CPE (Indoor/Outdoor), Smartphones, Hotspots, Laptops, Industrial Grade CPE/Router/Gateway), […]
Verizon customers will soon see yet another fee increase on their next bill
Verizon subscribers will soon experience yet another increase in fees on their upcoming bills, a common tactic among wireless providers. […]
6G: What It Is, How It Works, When It Will Launch
Data transfer via mobile phone is getting faster and faster. The new 5G network has not even been fully built […]
Optical fiber cable for 5G and future 6G network technology
One year after the presentation of the “GigabitStrategy” for the expansion of high-speed Internet, many projects have been completed. The […]
LiFi is a new technology that uses light sources to transmit data
Press the light switch, and the data flows. This is not science fiction, but the idea of an inventor. It […]
Samsung’s smartphone shipments decreased by 15.4 percent in the April-June period
Samsung Electronics has publicly apologized and recognized that the company is viewed as being in a “crisis” after announcing profit […]
What Is Cyberbullying? Cyberbullying is the use of technology to harass, threaten, embarrass, or target another person
According to a study, almost two million schoolchildren are affected by cyberbullying. It is now a “permanent problem”. The coronavirus […]
If loneliness can be a risk to health, shouldn’t more be done to address it? People can socialize again with the help of robots
Loneliness is a state of mind linked to wanting human contact but feeling alone. People can be alone and not […]
Apple iPhone 16 Pro Max vs Huawei Mate XT
Huawei Mate XT Ultimate Design smartphone debuted on September 10, 2024. The device features a 6.40-inch primary display with a […]